
Paul Kostek, IEEE Senior Member and Principal Systems Engineer with Air Direct Solutions LLC, discusses the potential of AI and robotics within healthcare.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics have shown themselves to be critical in aiding healthcare professionals in the ongoing fight against the COVID-19 pandemic. AI has enabled speedier and more efficient analysis of patient data, therefore allowing medical professionals to decipher medical conditions and the treatments as required.
Telehealth, or virtual appointments, have been utilised more widely throughout the pandemic. This service has been used for decades by those that live in remote areas but was regularly done by telephone, rather than videoconferencing. With the pandemic and the need for social distancing, telehealth has become an essential part of healthcare services, and has therefore been improved greatly throughout the pandemic as a result of necessity.
Telesurgery is the next endeavor which is being researched and could be used in the provision of urgent care.
AI and robotics have the potential to provide a range of services for patients, and will likely become more widely adopted in the future. One person championing the use of AI and robotics in healthcare is Paul Kostek, IEEE Senior Member and Principal Systems Engineer with Air Direct Solutions LLC. Here, he speaks to Health Europa about the impacts that AI and robotics have had upon healthcare and how this technology could be developed in the future.
In which areas of healthcare do you see AI and robotics having the biggest impact?
Throughout the pandemic, AI has proven to be an important resource for assessing data from patient scans and identifying treatment options. It has also been used to improve administrative operations of hospitals and medical centres. We may see more uses on the business side of the medical providers before the wider use in medical procedures.
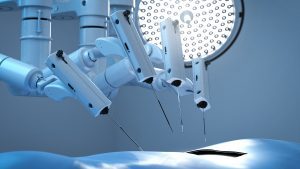
The current use of robotics in surgery allows doctors to perform minimally invasive surgery and limits the impact of a procedure while improving outcomes. Expansion of surgery automation will continue, incorporating AR and VR to improve performance. Telesurgery is the next step being studied and – in theory – provides access to a surgeon with a specialty not in the patient’s local area. This would eliminate the need for a patient to travel and could also be used when a patient needs immediate care. Challenges would include latency and the need for a surgical team to support the procedure in the event a problem arises.
How can these technologies be used to alleviate inefficiencies within the healthcare sector?
AI can help identify a patient’s condition and recommend possible care options and treatments. This can save doctors doing the research and, in turn, more time can be spent assessing the options presented by AI and discussing these with the patient. Robotic surgery can expand the options for a patient and improve outcomes by providing access to surgery in a local or versus travelling.
How can AI be used to help manage the COVID-19 pandemic?
With the pandemic, AI has been used to assess data from patient’s lung scans, to improve treatment options, identify variants and make changes to the treatments in use.
What key features are necessary to ensure AI programs are human-centered?
The ongoing challenge with AI is ensuring that the developers consider a wide range of subjects such as race and sex, so that the resulting diagnosis and treatment options fit the person’s needs. This requires AI developers to come from a wide range of groups and backgrounds, so they are not limited.
Looking ahead, how do you expect AI and robotics to redefine the role of the health professional? How can we best prepare the future healthcare workforce for the impact of AI and robotics?
AI and robotics are a key resource for health professionals, helping them focus on patients with research symptoms and treatments. Robotics have already been successfully limiting the impact of surgery, resulting in improved outcomes. We can expect the next step to be telesurgery, which will allow surgeons to provide treatment without the need for patient or doctor travel. In fact, in a few years there may well be surgery performed without the need for a surgeon. COVID-19 has demonstrated that the adoption of technology can happen much faster than expected and we will likely continue to see this occur.
Paul Kostek
IEEE Senior Member and Principal Systems Engineer
Air Direct Solutions LLC
www.ieee.org/
https://www.linkedin.com/in/paulkostek
This article is from issue 19 of Health Europa Quarterly. Click here to get your free subscription today.







