As a result of the rising demand for therapeutic medications, medicinal mushrooms have become increasingly important in healthcare over the last ten years.
The rapid evolution of the environment in which we live in, introduces novel diseases every single day which are harder and harder to treat. Our constantly changing surroundings and technological emphasis frequently reduce our body capacity to fight off these diseases as our immune systems deteriorate. The majority of medications used in modern medicine are made of synthetic substances with negative side effects. Natural medicine mimics human biology as it adapts to the always changing environment, just as nature does.
Since ancient times, people have used mushrooms as a source of traditional medicine since they are recognised to be a treasure trove of natural bioactive ingredients. Terpenoids, a sizable class of bioactive metabolites produced by mushrooms, have recently attracted scientific interest as potential therapeutics with qualities such as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-neurodegenerative, antioxidant, and antiviral.
Common Mushrooms
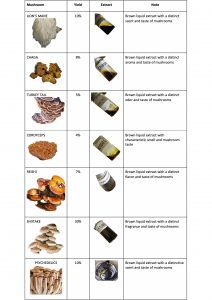
There are different varieties of mushrooms. Only a small number from more than 10,000 diverse mushroom kinds have strong scientific evidence for their health advantages. These are the ones that, in our opinion, can actually help.
Lion’s Mane
A huge, white mushroom known as “lion’s mane” develops a shaggy appearance that resembles a lion’s mane. According to studies, lion’s mane helps raise Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) levels, which shields us from memory-damaging degenerative brain conditions. Studies have shown that lion’s mane helps lessen irritation and anxiety, while it is best recognised for enhancing memory and attention. Additionally, numerous research have suggested that lion’s mane possesses immune-boosting properties. When we breathe in, harmful microorganisms enter the body through the mouth or nose. By encouraging gut microorganisms to activate the immune system, lion’s mane can aid to strengthen our defences.
Chaga
Chaga has been utilised for millennia as an immune system booster all throughout the world. The immune system’s initial line of defence is made up of white blood cells. Studies have revealed that the Chaga mushroom controls cytokines, a protein that promotes the formation of white blood cells. High levels of zinc in this antioxidant-rich mushroom support the immune system’s ability to fight off viruses and germs. Triterpenes and sterols such inotodiol, trametenolic acid, and betulinic acid, among others, can be isolated with the help of the chaga mushroom.
Maitake
In Asia, maitake is revered for its extensive medicinal virtues. Because they are so enamoured with this fungus’s health advantages, the Japanese gave it the name Maitake, which translates to “dancing mushroom,” as soon as they learned of it. One category of adaptogen is maitake. By reducing any physical and mental stress you may be experiencing, it aids in the body’s achieving its ideal state of balance. According to studies, persons who experience chronic fatigue syndrome may benefit from it. Recent research has demonstrated that maitake can assist in triggering T cells and natural killer cells in the immune system.
Reishi
Reishi has become one of the most well-liked medicinal mushrooms to encourage a state of relaxation in today’s environment of stress and worry. Triterpene, an active ingredient in Reishi, has been found in research to help lower stress, promote restful sleep, elevate mood, and sharpen mental focus. Reishi contains a triterpene that has been demonstrated in tests to improve immune response by boosting the activity of natural killer cells, which are white blood cells that fight infections. Triterpenes are in charge of giving Reishi mushrooms their bitter flavour, which is a sure-fire indicator of a high-quality Reishi mushroom.
Cordyceps
A Chinese fungus called cordyceps is utilised as a restorative tonic. Additionally, it is renowned for enhancing athletic performance. It is more convenient to get cordyceps extracts in liquid or capsule form rather than whole, dried cordyceps, which you can add to soups and stews or use to make tea. Take cordyceps once or twice a day as directed by the product’s label to treat general weakness. You should take it once or twice every week to maintain your health.
Shiitake
Shiitake mushrooms, which are mostly farmed in Japan, are prized for their exceptional flavour and have been sought after for thousands of years by people hoping to lengthen their lifespan and reduce inflammation. Shiitake mushrooms are very high in B vitamins and contain antiviral and antibacterial characteristics, which is why they are so effective. Shiitake mushrooms may aid in preventing and reducing body weight increase and fat storage. Furthermore, a current study indicated that shiitake can assist improve cell function, gut immunity, immunological function, and reduce inflammation. This study was recently published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition.
Psychedelics
Magic mushrooms, often known as psilocybin, are ingested for their hallucinatory effects. They are psychedelics, a class of substances that cause alterations in perception, mood, and thought. Psilocybin is the active component of magic mushrooms. When psilocybin is consumed, it is transformed in the body into psilocin, the substance that has psychedelic effects. Nevertheless, psilocybin continues to show promise in clinical trials for the treatment of mood, anxiety, and substance use problems.
Therapeutic values of medicinal mushrooms
It’s not always the same compounds that make up the mushrooms’ medications. Some are polysaccharides, which have longer chains of connected sugar molecules, while others are triterpenoids, which have three units hand-in-hand. Among other things, terpenoids from mushrooms have shown to have anticancer, antiviral, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory activities. In a 2015 study, 285 terpenoids that could be used medicinally were identified from medicinal mushrooms.
One terpene with the names lucialdehyde D and ganoderone A, for instance, has been shown to exhibit antiviral activities against the influenza A and herpes simplex type I viruses. Hydnellum scabrosum, also known as Sarcodon scabrosus, is a bitter hedgehog mushroom that contains diterpenoids known as scabronines, sarcodinians, and sarcodonin G that can halt the proliferation of human cancer cell lines and therefore the spread of the disease. In ovarian, glioma (brain and spinal cord cancer), and melanoma (skin cancer) cells, to name a few, this characteristic has been demonstrated.
The top three health benefits of polysaccharides found in medicinal mushrooms were anticancer, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory effects. Polysaccharides can also enhance intestinal health in people. These excellent studies demonstrate the medicinal use of mushrooms and support further investigation into the chemical makeup of the plants by extraction. In contrast to most terpenes and lipophilic (fat-loving) cannabinoids, triterpenes are typically soluble in water. However, polysaccharides are less straightforward and may require a variety of extraction techniques.
In a 2014, paper that appeared in the journal Microbiology, the beta-glucan content of both fruiting bodies and mycelia was examined. According to the study, mushrooms grown on a mycelium basis have up to 100% less beta-glucans than mushrooms produced on fruiting bodies. This study adds to the body of evidence indicating fruiting bodies contain up to 2.5 times as many beta-glucans as mycelia, according to a second study from 2011 that was published in the journal Food Chemistry. We advise choosing a supplement that includes only extracted fresh complete fruiting bodies in order to get the best effects.
Extracting
A few factors need to be considered during the extraction of a mushroom’s bioactive substances: flavour, consistency, and yield. Without a doubt, the core of all our mushroom extracts is alcohol extraction. It functions but has a terrible flavour. Because of this, there are many more cutting-edge solventless processes, which we will cover below, that gently extract while maintaining outstanding taste and consistency.
Understanding chitin is another crucial aspect of mushroom extraction. The element that makes up the fungal cell wall is chitin. The majority of the mushroom taken as food is converted to insoluble fibre because the human body does not naturally manufacture the chitinase enzyme required to break down chitin. In this case, mushroom extraction is important. By following the right extraction techniques for medicinal mushrooms, we may dissolve this chitin and provide our bodies simple access to the essential components that are inside. The essential triterpenes, sterols, beta-glucans, and other helpful substances become more accessible.
Different solvents must be used for the extraction of different mushroom components. For instance, beta-glucans must be extracted using hot water since they are water-soluble, and the body cannot absorb them otherwise. Triterpenes, on the other hand, must be extracted using an alcohol solvent in order for them to be bioavailable because they are alcohol soluble. Certain mushroom types require the use of only water for extraction because beta-glucans are the main active component. The greatest choices for dual extraction are other kinds since they have significant triterpene and beta-glucan concentrations.
Independent of their physical and chemical properties, all of the compounds present in a mushroom extract are referred to as “full spectrum” substances. This consists of many substances from the mushroom extract, including both water-soluble and non-water-soluble ones. A full spectrum product benefits from “the entourage effect” of the whole food by promoting the full spectrum of bioavailable compounds in a mushroom.
Warm water
The most widely used extraction technique for mushrooms uses hot water, which is an extremely old and conventional technique. If you don’t bother about the remaining water in the extract, this is the simplest extraction and the basis for preparing any meal.
Etanol
Pure alcohol alone is not used very often when making medicinal mushroom powder. Dual extracts or double extractions are used when both water and alcohol are used in the extraction procedure. The extraction method that produced the highest yields was one that included ethanol and water. The tiny levels of volatile chemicals in the mushroom powder are demonstrated by the fact that maceration in pure ethanol produces a yield that is significantly lower than that of mixed solvent extraction and almost nothing. This method of extraction still has two significant drawbacks: first, ethanol denatures all essential molecules, and second, it is painful to remove the ethanol and deal with the resulting bad taste.
CO2
The same goes for sCO2 and hexane. Lower polarity than ethanol are provided by dichloromethane and ethyl acetate. Consequently, yields decreased as polarity decreased. Lower extraction yields were found by sCO2, which was not surprising. A higher density of mushroom produced better yields because the ability of sCO2 to solubilise components in the mushroom was correlated to its density. Naturally, at the greatest ethanol concentration, the addition of ethanol boosted extraction yields approximately four-fold. By using sCO2, you can only extract dry, powdered mushrooms, missing out on many of the active terpenoids that are present in fresh mushrooms. Additionally, the issue of getting rid of the ethanol and coping with the unpleasant taste still exists.
Aerosols
It has been demonstrated that PURE5‘s aerosol extraction method gently extracts oleoresins from a variety of plants, including medicinal mushrooms. Aerosol extracts are produced at room temperature without degrading the oil and maintaining its full potency. The results are considerably better than any other extraction implemented for this market as none of those extracts the whole target active components. Aerosols offer a number of advantages over “traditional” solvents, such as the ability to capture volatiles that aren’t lost with the solvent, a reduced risk of extracting colours and other undesirable compounds, and the use of low temperatures to safeguard delicate, labile constituents. High yields are produced, and the flavour is similar to that of a wild mushroom.
Results
Antioxidant, immune system support, glucose regulating effects, nerve pain, brain function and support, anti-inflammatory, gastrointestinal, and many more medical qualities are just a few of the qualities.
Mushrooms are unique plants that can deliver many nutritional and health values to our being. In addition, the easy cultivation and low energy requirements makes them for sure a subject for farming all over the country. The proper combination of proteins, triglycerides, fibre and terpenes can put the mushroom high in the food chain. Using the latest state of the art technology it is essential to reuse all components of the mushroom without destroying the other parts. With the PURE5 solventless gentle ambient temperature extraction the mushroom can be extracted while fresh then further processed for its nutritional values. Staying away from chemicals that destroy the vital components and being organic in all aspects is the target for future food processing.